Appearance
Data Warehouse Instances
A Yellowbrick instance is a deployed and provisioned data warehouse that runs in a SaaS cloud environment. After logging into the Yellowbrick Manager for the first time, you will be prompted to create your first instance.
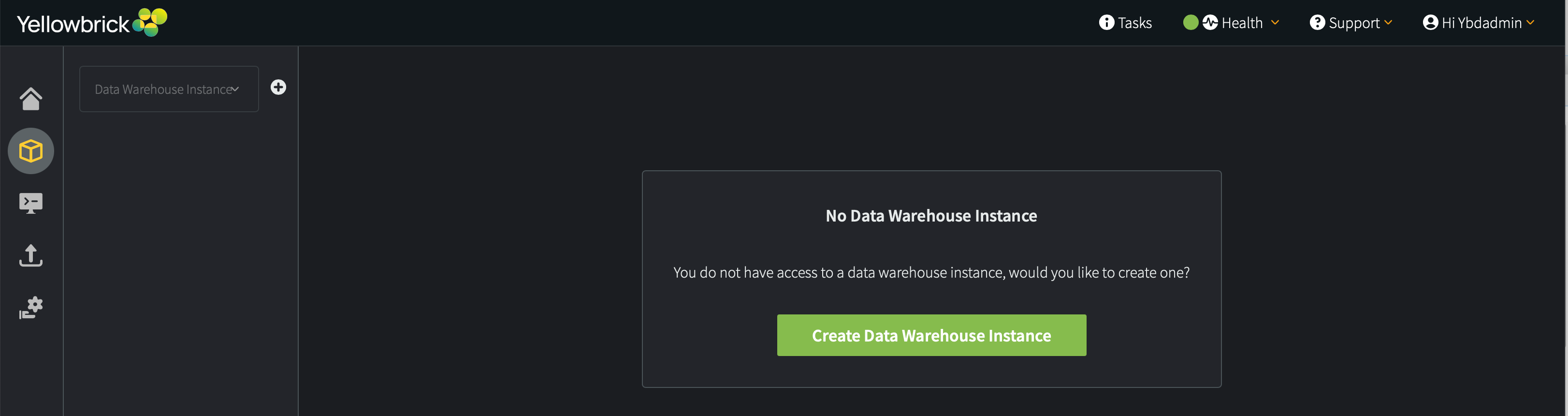
When you create a new instance for an AWS deployment, you will be prompted to choose the shared services type: Standard or Scaled. This option is not available for Azure deployments. See Shared Services Type.
Note: Instance names must be 2 to 63 characters long and contain only alphanumeric characters and hyphens (-). Hyphens may not be in first or last position in the name, and may not be repeated successively. Hyphens should only be used as "separators."
For example, the following instance names are valid:
bobr-inst1-080222yb60-cdwm318-august2-2022yellowbrick60instance100
You can create multiple instances in order to set different hardware limits for different users and workloads. Each instance defines the region and the supported hardware instance types (optional limits for creating hardware resources that will be allocated to and shared among virtual compute clusters).
For simplicity and usability, "small" and "large" instance types are supported, where the large nodes use hardware with more cores per CPU, more RAM, and a bigger data cache.
small-v1:m5dn.4xlargein AWSStandard_L16s_v3in Azuresmall-v2:i4i.4xlargein AWSlarge-v1:i3en.metalin AWSStandard_L80s_v3in Azurelarge-v2:i4i.32xlargein AWS
You can reserve some number of nodes when you create instances. After creating an instance, you can change the number of reserved nodes and/or the maximum number of nodes available to the clusters in the instance. This option provides a way to scale an instance up or down.
There is also a per-instance database storage option. If you accept the default behavior for Create internal external storage, object storage for the data stored in your databases and tables will be created automatically. If you deselect this option, you have to create your own "primary storage" by using the CREATE EXTERNAL STORAGEandCREATE EXTERNAL LOCATION commands.
For example, in Azure:
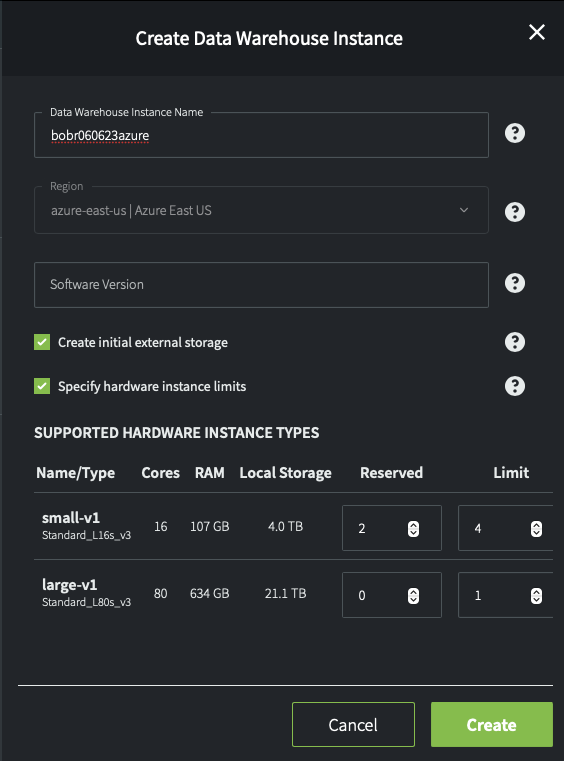
Local Storage refers to the size of the SSDs (that is, a limit on the data cache, not physical storage).
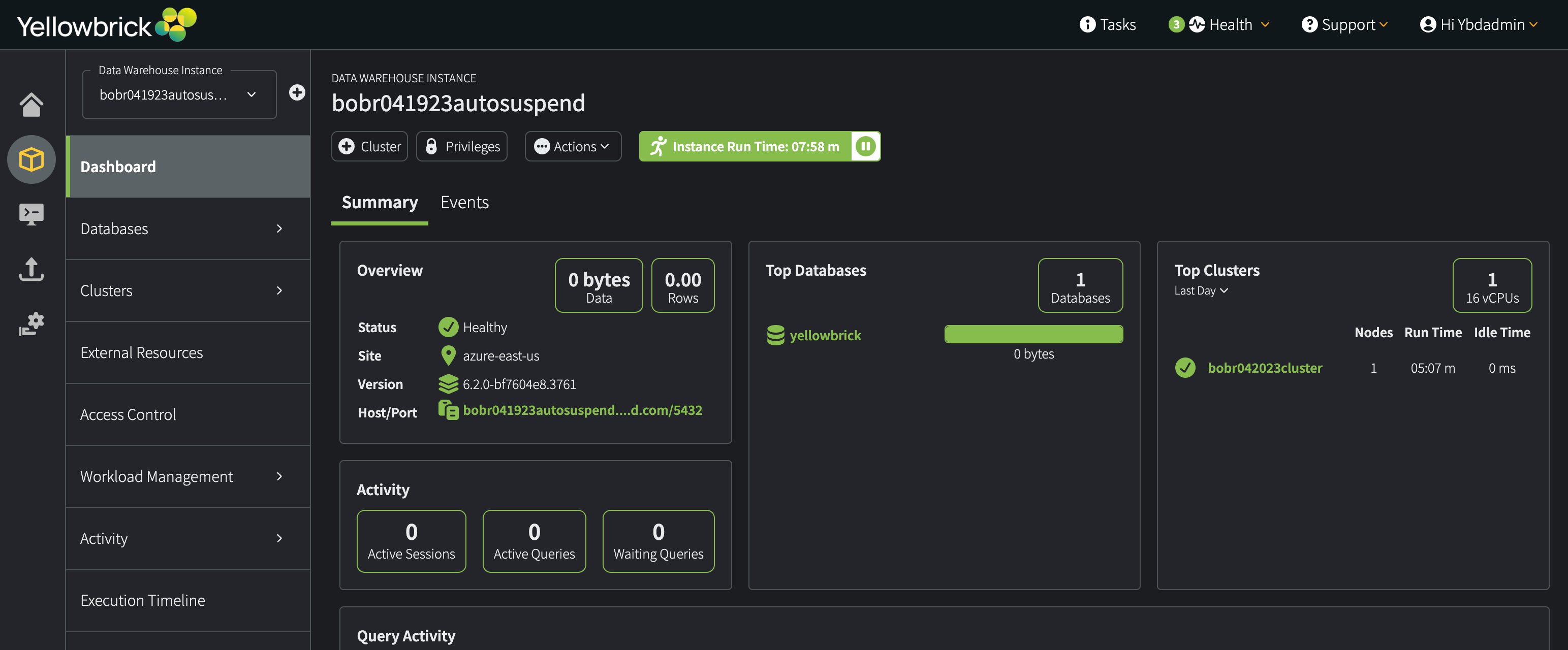
On the Dashboard, you can see details about your instances. Three useful pieces of information are:
- Status (
Healthywhen available for use) - Site (region name)
- Host/Port, a connection string that you can copy to the clipboard and use to connect client applications to this instance
For example:
Note: The default time zone for data warehouse instances is set to UTC (timezone and log_timezone configuration parameters).
In This Section
Parent topic:Provisioning the Data Warehouse