Appearance
EXPLAIN
Return the text version of the query plan for either a specific SELECT query or a statement that runs a query.
Use the SMC to see a graphical version of the plan.
Syntax
EXPLAIN ( [ ANALYZE ] [ , VERBOSE ] [ , STABLE ] [ , TYPE ] ) query- ANALYZE
Run the query and return both the query plan and execution details. Runtime statistics are reported, including rows returned, execution time (in milliseconds), memory use, and cache hits. The read efficiency statistic is a percentage that describes how effective the execution engine was in not reading rows from the storage engine early in the plan. A value of 0% means that no rows were discarded in this way. A high value means that the system was very efficient and incurred less I/O. Sorting a table on a column that is frequently constrained may influence read efficiency.
If you do not specify this option, EXPLAIN returns the query plan without running the query.
Warning: Running
EXPLAIN ANALYZEon anINSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEstatement modifies the target table, without warning. To avoid this problem, you can run theEXPLAIN ANALYZEstatement inside a transaction, then roll it back if needed. See EXPLAIN ANALYZE for a DELETE.- VERBOSE
Return a more detailed plan output. You can use this option with or without
ANALYZEand/orSTABLE.- STABLE
Strip out details that might vary in the plan. Only the basic structure of the plan is rendered, regardless of actual statistics. You can use this option to isolate real differences between plans when the same query is run multiple times under different conditions. You can use this option in conjunction with
VERBOSEand/orANALYZE.Note:
LIMITqueries that do not have anORDER BYclause are non-deterministic; therefore, using theSTABLEoption for these queries is not recommended.- TYPE
Return the data types for the columns in the output.
- query
Any valid Yellowbrick query. You can run the EXPLAIN command on all of the following query statements:
- SELECT
- SELECT INTO
- CREATE TABLE AS (CTAS)
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
You cannot run the EXPLAIN command on a TRUNCATE statement.
Return the plan for a SELECT * query
premdb=# explain select * from awayteam;
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------
id rows_planned workers node
0 50 single SELECT
(awayteam.atid, awayteam.name)
distribute none
2 50 single SCAN awayteam
(awayteam.atid, awayteam.name)
distribute single
(8 rows)Run the same query and return both the plan and statistics
premdb=# explain (analyze) select * from awayteam;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Planning time: 0.069 ms
id rows_planned rows_actual skew memory workers node
0 50 50 0.00 512.14k single SELECT
distribute none
2 50 50 0.00 20.00k single SCAN awayteam
distribute single
read_efficiency=0.0%
50 rows returned, read 0.05MB, distributed 0.00MB, memory used 12.58MB
Code cache hits: 0/2, lookup cache hit: false
Execution time: 563.696 ms
(10 rows)Run the same query and add the VERBOSE option
premdb=# explain (analyze, verbose) select * from awayteam;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Planning time: 0.062 ms
id rows_planned rows_actual skew memory workers node
0 50 50 0.00 256.14k single SELECT
(awayteam.atid, awayteam.name)
distribute none
2 50 50 0.00 20.00k single SCAN awayteam
(awayteam.atid, awayteam.name)
distribute single
read_efficiency=0.0%
50 rows returned, read 0.05MB, distributed 0.00MB, memory used 12.58MB
Code cache hits: 1/1, lookup cache hit: false
Execution time: 20.513 ms
(12 rows)Return the plan for a query that filters rows returned from a sorted table
Note the read efficiency statistic in this example. (The table newmatchstats is sorted on seasonid.)
premdb=# explain (analyze) select * from newmatchstats where seasonid=10;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Planning time: 0.091 ms
id rows_planned rows_actual skew memory workers node
0 34200 34200 0.00 1.00M all SELECT
distribute none
2 34200 34200 0.00 36.00k all SCAN newmatchstats
distribute on (newmatchstats.seasonid)
scan_constraints: (newmatchstats.seasonid = $0)
read_efficiency=41.0%
34200 rows returned, read 1.49MB, distributed 0.75MB, memory used 14.68MB
Code cache hits: 0/2, lookup cache hit: false
Execution time: 705.108 ms
(11 rows)Use the STABLE option on the previous query
premdb=# explain (analyze, stable) select * from newmatchstats where seasonid=10;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Planning time: 0.112 ms
rows_actual workers node
34200 all SELECT
distribute none
34200 all SCAN newmatchstats
distribute on (newmatchstats.seasonid)
scan_constraints: (newmatchstats.seasonid = $0)
34200 rows returned
(8 rows)Add the TYPE option to the previous query
premdb=# explain (analyze, stable, type) select * from newmatchstats where seasonid=10;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rows_actual workers node
34200 all SELECT
(newmatchstats.seasonid INT2, newmatchstats.matchday DATE, newmatchstats.htid INT2, newmatchstats.atid INT2, newmatchstats.moment VARCHAR(5))
distribute on (newmatchstats.seasonid)
34200 all SCAN newmatchstats
(newmatchstats.seasonid INT2, newmatchstats.matchday DATE, newmatchstats.htid INT2, newmatchstats.atid INT2, newmatchstats.moment VARCHAR(5))
distribute on (newmatchstats.seasonid)
scan_constraints: (newmatchstats.seasonid = $0)
34200 rows returned
(9 rows)EXPLAIN ANALYZE for a DELETE
This example shows the behavior to expect when you use the ANALYZE option on a statement that writes data. In this case, three rows are deleted from the season table. If you run this type of EXPLAIN command but do not want to delete, insert, or update the data permanently, wrap the EXPLAIN ANALYZE statement inside a transaction so that the changes can be rolled back.
premdb=# select count(*) from season;
count
-------
25
(1 row)
premdb=# explain analyze delete from season where winners='Arsenal';
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Planning time: 0.265 ms
id rows_planned rows_actual skew workers node
3 3 3 0.54 single DISTRIBUTE RANDOM
4 3 3 1.00 single DELETE FROM season
5 3 3 1.00 all DISTRIBUTE WORKER
7 3 3 0.00 all SCAN season
season.winners = $0 AND scan_constraints: (season.winners = $0)
read_efficiency=0.0%, rows_from_column_store=3, rows_from_row_store=0
3 rows deleted
Read: 1.52MiB, Distributed: 72.00B, Write: 240.00kiB
Database: premdb
Version: 5.3.4-20211123225935
Hostname: yb04-mgr0.yellowbrick.io
query_id: 5249610
Lookup cache hit: false
Code cache hit: true
Execution time: 128.120 ms, End time: 2021-11-29 14:58:35
(17 rows)
premdb=# select count(*) from season;
count
-------
22
(1 row)SMC Graphical EXPLAIN
Tip: You may also want to use the visual EXPLAIN feature in the System Management Console (SMC). After logging in, go to Monitor, then Active Queries or Query Performance, double-click the query you want to explain, and click Plan. For example:
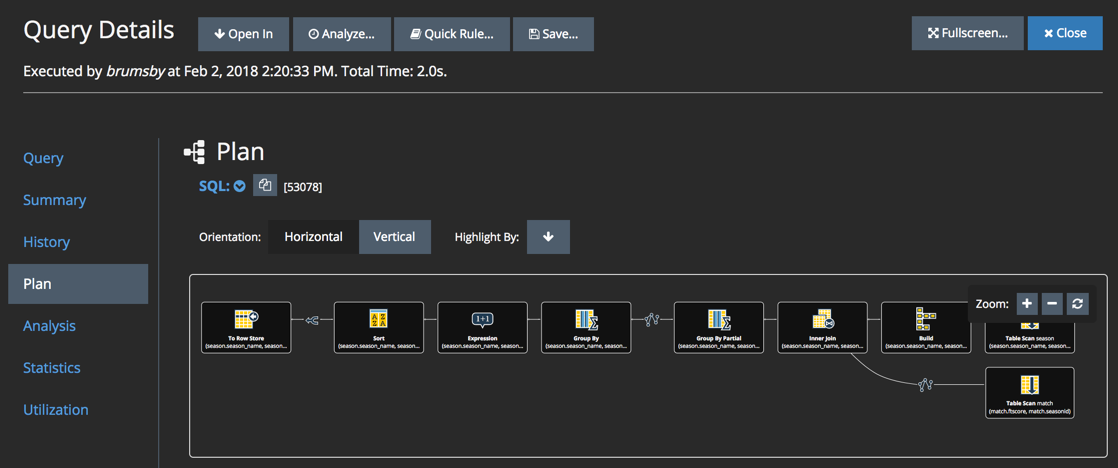
Parent topic:SQL Commands